|
Bleeding symptoms, other than from injuries, are often seen in many medical conditions. Blood escapes from the blood vessels into the body that causes internal bleeding, or out of the body through openings such as vagina, mouth, nose, ear, anus or wounds. Unexplained bleeding or frequent bruising may be a sign of underlying health problems that require medical attention.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a unique understanding about how bleeding develops, and has accumulated extensive experiences in treating bleeding conditions. TCM methods can be a choice for controlling bleeding that complicates in various medical conditions, especially for mild to medium bleeding cases.
1. TCM views on the development of bleeding
In TCM, blood is viewed simply as the red fluid circulating within the vessels; it relies on the regulations of internal organs to distribute efficiently throughout the body. Blood is transformed by the spleen; stored by the liver; pushed by the heart; disseminated by the lungs; and transformed into life essence by the kidneys. Moreover, qi (vital energy) plays an essential part in the blood activities; qi not only moves blood around the body, but also helps promote its production and hold it in the vessels as well. Internal disharmonies that are likely to develop bleeding complications are:
 |
Qi deficiency: makes the blood vessels become fragile and unable to contain blood; |
 |
Excessive heat: damages the blood vessels and results in “reckless” movement of hot blood; |
 |
Blood stasis: causes obstructions in the blood vessels and forces blood to outflow from its normal pathways. |
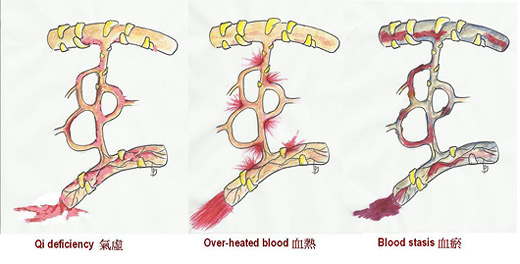 |
TCM views on the development of bleeding |
Generally, the above can be due to external pathogens, improper diet, emotional strain or internal organ problems; these factors affect different body regions, organs and meridians, and lead to a variety of types of bleeding.
Invasion of external pathogens
External pathogens are related to seasons or environment. When external heat evils attack the blood system and damage the blood vessels, it will cause blood to exude. For other pathogens like coldness, dampness or wind, they usually join up with heat evils or transform into internal heat evils when causing bleeding. Wind, heat and dryness evils are likely to affect the upper body and cause symptoms such as nosebleeds, coughing up blood and vomiting blood. While vaginal bleeding, bloody stool or blood in the urine that occur in the lower body can also due to damp-heat evils. Pestilential evil is a kind of pathogenic factor with intense infectivity, which can lead to bleeding under the skin.
Improper diet
Improper diet such as over consumption of alcohol, hot and spicy foods can make the intestines accumulate heat or damp-heat evils. When the pathogens damage the blood vessels, disturb the flow of blood, there will be vomiting blood, nosebleed or bloody stool. Moreover, unhealthy diet habits also weaken the spleen, affect its production of qi (vital energy), and make the body unable to keep blood flowing properly inside the vessels, resulting in bleeding.
Emotional strain
Excessive and prolonged emotional problems are considered the major internal causes of disease in TCM. Anger or stress impairs the movement of qi and leads to liver stagnation, which can interfere with stomach function, and result in vomiting blood. As time passes, a stagnated liver will generate fire that may attack the lungs and cause coughing up blood or nosebleeds. On the other hand, excess anxiety or over thinking disturbs the heart, which generates fire to irritate the bladder or small intestine, leading to blood in the urine.
Unbalanced lifestyle
Anything undertaking to extreme will harm the body and result in disharmony. For example, over-thinking impairs the heart; too much physical work impairs the spleen; unlimited sexual activities impair the kidneys. An overstrained body usually presents with qi and yin deficiencies. Qi deficiency can make the body fail to keep the blood flowing properly; while yin deficiency can cause the body to create virtual fire and also affect blood flow.
Feverish and chronic diseases
Feverish and chronic diseases consume the fundamental substances of the body and may result in bleeding problems. For example, depletion of body fluids or blood leads to yin deficiency; when virtual fire is generated and damaged the blood vessels, bleeding will occur. Qi depletion is common during the development of diseases, there will be insufficient qi to keep blood flow properly within the vessels, and blood can escape easily. Furthermore, a prolonged illness usually involves the formation of blood stasis that forces blood to outflow from it normal pathways.
2. TCM diagnostic criteria for bleeding symptoms
Bleeding is a symptom that needs to consider its underlying medical condition when making diagnosis and giving treatment. Abnormal bleeding can occur in different medical conditions and present with different clinical characteristics. TCM physicians will consider the bleeding site, characteristics of bleeding, primary condition, and accompanying signs to identify a disharmony pattern as clinical diagnosis. Below are TCM diagnostic criteria for bleeding symptoms.
Characteristics of bleeding and accompanying signs are important for determining the internal disharmonies.
Disharmonies |
Clinical characteristics |
Heat stirring blood vessels |
This usually occurs in the early stage of a bleeding problem. Acute onset, the bleeding is quite heavy, the blood looks bright red and thick in texture, or dark-red patches on the skin, the accompanying signs are fever, irritability, thirst, constipation, yellowish urine, a hot sensation during urination, and a red tongue with yellow coating |
Yin deficiency creating virtual fire |
The bleeding starts gradually, lasts a long period of time or recurrence, the accompanying signs are hot flushes in the evening, mouth dryness, warm palms and soles, irritability, red cheeks, night sweats, dizziness, ear ringing, lumbar soreness, knee weakness, and a red tongue with little coating |
Qi deficiency failing to retain blood |
Individuals usually have a prolonged bleeding condition. The bleeding starts gradually, lasts a long period of time, and the blood looks thin in texture. The accompanying signs include pale or swallow complexion, fatigue, general weakness, dizziness, ear ringing, insomnia, sweating, breath shortness, palpitations, a pale and bulky tongue with teeth marks on the margin, and a weak and thready pulse |
Blood stasis obstruction |
Beside the above characters, there may have fixed or localized pain, the blood looks dark-red in color or clotted, dark-purplish spots or patches on the skin, a dull complexion, abdominal mass, a dark-purplish tongue and hesitant pulse |
Bleeding sites are closely linked up with the functional states of certain organs and their corresponding meridians. Identifying the major involved organs will help determine what specific functions need to be restored.
Bleeding sites |
Major involved organs |
Nose bleeding |
Lungs, stomach and liver |
Gum bleeding |
Stomach and kidneys |
Conjunctiva bleeding |
Lungs |
Tongue bleeding |
Heart |
Coughing up blood |
Lungs |
Vomiting blood |
Stomach and liver |
Blood in the stool |
Stomach and intestines |
Blood in the urine |
Heart, liver and kidneys |
Blood in the semen |
Kidneys and liver |
Uterine bleeding |
Kidneys and spleen |
Bleeding under the skin |
Spleen |
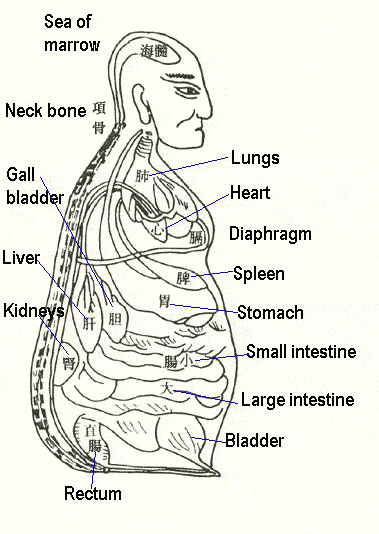 |
TCM internal organs |
3. TCM therapeutic principles of bleeding symptoms
No matter what medical conditions cause abnormal bleeding, TCM treatment always focuses on clearing fire/heat evils, improving qi (vital energy) and blood conditions, and a harmonized blood is the ultimate goal of all. Physicians have to follow some general principles when designing the herbal prescriptions.
Treat the root-cause
Since each bleeding symptom has an underlying disharmony, it should be identified clearly, so as to find a matched formula, and combine the herbs to address individual conditions exactly. Generally, the remedies are aimed to clear heat, cool blood, replenish qi, reinforce the astringent ability of qi, nourish yin, subdue virtual fire, activate blood or remove stasis.
Select stop-bleeding herbs
Although the herbs can stop bleeding, they only play an auxiliary role. They should never be used on their own, and must always be combined with herbs that treat the underlying disharmony of bleeding. The herbs are selected according to their natures, such as cooling blood, warming blood, activating blood or astringent. Each herb can have more than one of these effects.
Effects |
Sample herbs |
Indicated bleeding signs |
Cooling blood to stop bleeding |
Rhizoma Imperatae (bai mao gen)
Cacumen Platycladi Orientalis (ce bai ye)
Herba Cirsii Japonici (da ji)
Herba Cirsii (xiao ji)
Radix Sanguisorbae (di yu)
Flos Sophorae (huai hua)
Radix Rubiae (qian cao) |
The blood is bright red |
Activating blood to stop bleeding |
Radix Notoginseng (san qi)
Pollen Typhae (pu huang)
Nodus Nelumbinis Rhizomatis (ou jie)
Radix Rubiae (qian cao)
Faeces Trogopterorum (wu ling zhi)
Radix Curcumae (yu jin)
Crinis Carbonisatus (xue yu tan)
Crotex Moutan (mu dan pi) |
The blood is clotted |
Astringent bleeding |
Rhizoma Bletillae (bai ji)
Herba Agrimoniae (xian he cao)
Petiolus Trachycarpi (zong lu tan)
Os Sepiae (wu zei gu)
Nodus Nelumbinis Rhizomatis (ou jie)
Crinis Carbonisatus (xue yu tan) |
Profuse or prolonged bleeding |
Warming blood to stop bleeding |
Rhizoma Zingiberis Praeparatae (pao jiang)
Folium Artemisiae Argyi (ai ye)
Furnace soil (fu lung gan) |
The blood is light, and accompanied with limb coldness or sensitive to low temperatures |
Nourishing blood to stop bleeding |
Colla Corii Asini (e jiao)
Colla Cornus Cervi (lu jiao jiao)
Herba ecliptae (han lian cao)
Fructus Ziziphi Jujubae (da zao) |
Bleeding accompanied with dizziness, palpitations and swallow complexion |
Apart from the category of stop-bleeding herbs, herbs from other categories are also used for this purpose. In addition, some of the stop-bleeding herbs have a tendency to work on specific body regions, reach certain organs or meridians, and thus are usually selected for specific bleeding symptoms.
Bleeding locations |
Sample herbs |
Wound bleeding on the body surface (topical use) |
Radix Notoginseng (san qi)
Rhizoma Bletillae (bai ji)
Lasiosphaera Seu Calvatia (ma bo) |
Nosebleeds |
Rhizoma Imperatae (bai mao gen)
Herba Agrimoniae (xian he cao)
Nodus Nelumbinis Rhizomatis (ou jie)
Herba Cirsii (xiao ji) |
Gum bleeding |
Rhizoma Imperatae (bai mao gen)
Herba Agrimoniae (xian he cao)
Nodus Nelumbinis Rhizomatis (ou jie) |
Coughing up blood |
Rhizoma Bletillae (bai ji)
Herba Agrimoniae (xian he cao)
Rhizoma Imperatae (bai mao gen) |
Vomiting blood |
Os Sepiae (wu zei gu)
Rhizoma Bletillae (bai ji)
Radix Sanguisorbae (di yu) |
Blood in the urine |
Herba Cirsii Japonici (da ji)
Herba Cirsii (xiao ji)
Radix Sanguisorbae (di yu)
Pollen Typhae (pu huang) |
Blood in the stool |
Radix Sanguisorbae (di yu)
Flos Sophorae (huai hua)
Radix Notoginseng (san qi)
Furnace soil (fu lung gan) |
Bleeding under the skin |
Peanut skin
Fructus Ziziphi Jujubae (da zao)
Charred lotus leaf |
Uterine bleeding |
Herba Agrimoniae (xian he cao)
Radix Rubiae (qian cao)
Pollen Typhae (pu huang)
Folium Artemisiae Argyi (ai ye) |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| couch grass rhizome |
|
carbonized hair |
|
Chinese date |
Consolidate and rebuild harmony
Bleeding symptoms are consumptive, which exhausts blood, qi and other fundament substances of the body. Physicians will consider the deficient aspects of the body and select appropriate supplement herbs for tonification accordingly. For example, massive or a prolonged blood loss usually leads to a blood deficiency state, it is applicable to add extra blood-nourishing herbs such as angelica root and rehmannia root. This can enhance the efficacy of the prescription and ensure a smooth healing process.
|