TCM believes that the major pathologies of ulcerative colitis include spleen and stomach dysfunctions, intestinal turbid accumulations, and blood and qi disturbances . Therefore, TCM treatment strategies are to restore organ functioning, eliminate turbid accumulations and harmonize the flows of qi and blood.
In clinical applications, if individuals have obvious pus, mucus or bloody loose bowels, physicians will focus on clearing pathogens like damp-heat or damp-cold, so as to improve the bowel environment. Afterwards, tonifying methods are employed to overcome the internal weakness and promote a longer remission period.
Damp-heat in the large intestine
Therapeutic aim: Clearing damp-heat, harmonizing blood and qi.
Sample prescription: Modified Peony Decoction (Shao Yao Tang)
In the prescription, the peony root and angelica root enrich the blood; the betel nut, costus root and rhubarb promote qi flow, the thread rhizome and skullcap root clear damp-heat and detoxify. The whole combination resolves the pathogenic accumulation in the large intestine, enabling the bowel to resume its normal transmission process.
 |
| Peony root |
Damp-cold in the spleen
Therapeutic aim: warming and dissolving dampness, harmonizing blood and qi
Sample prescription: Modified Weiling Decoction (Wei Ling Tang)
In the prescription, the atractylodes rhizome and root enhance fluid metabolism in the spleen; the magnolia bark and tangerine peel regulate qi flow to dispel damp-cold; the poria, water-plantain root and chu-ling induce urination; cassia bark and ginger promote warmth to expel coldness. The whole combination enables the intestinal functions to perform normally by enhancing spleen functioning and dispelling damp-cold pathogens.
Qi and Blood stagnation
Therapeutic aim: regulating blood and qi flows to arrest diarrhea and pain.
Sample prescription : Modified Decoction for Removing Blood Stasis in the Lower Abdomen (Shao Fu Zhu Yu Tang)
In the prescription, the cattail pollen, angelica, lovage and squirrel feces nourish blood and promote tissue regeneration; the corydalis rhizome, peony root and myrrh promote blood and qi flows to arrest pain; the fennel, ginger and cassia bark warm the meridian to dispel blood stasis. The whole combination improves the circulation in the large intestine so as to arrest diarrhea and pain.
Liver stagnation and spleen weakness
Therapeutic aim: soothing liver, invigorating spleen, expelling dampness, arresting diarrhea.
Sample prescription: Modified Essential Formula for Diarrhea with Pain (Tong Xie Yao Fang)
In the prescription, the atractylodes root invigorates the spleen; the peony root works on the liver; the tangerine peel regulates qi flow and expels dampness; the ledebouriella root assists the above herbs to work properly. The whole combination invigorates the spleen and expels dampness to arrest diarrhea, soothes the liver and regulates qi to arrest pain.
Spleen qi deficiency
Therapeutic aim: Replenishing qi, invigorating spleen, consolidating intestines to arrest diarrhea.
Sample prescription: Modified Powder of Ginseng, Poria & Atractylodes (Shen Ling Bai Shu San)
In the prescription, the ginseng, atractylodes root and poria are the main ingredients to replenish qi and invigorate the spleen; the hyacinth bean, coix seed, lotus seed and yam enhance the water metabolism of the spleen which helps to drain dampness and arrest diarrhea; the amomum fruit promotes the digestive process; the balloonflower regulate the water passages and the liquorice acts as a buffer.
Spleen and kidney deficiencies
Therapeutic aim: warming and tonifying the spleen and kidney, consolidating the intestine to arrest diarrhea.
Sample prescription: Modified Immortal Organ-Nourishing Decoction (Zhen Ren Yang Zang Tang)
In the prescription, the poppy capsule is used in high dosage to consolidate the intestine and arrest diarrhea; cassia bark warms the kidney and spleen; both herbs are the main ingredients. The nutmeg and myrobalan fruit provide warming to arrest diarrhea; the ginseng and atractylodes root replenish qi; the angelica and peony root replenish blood; the costus root and liquorice root act as buffer.
An enema is the procedure of introducing liquids into the rectum and colon via the anus. Herbal enemas help improve problems affecting the lining of the bowel such as abrasions, edema, ulcers and bleeding, therefore effectively relieving the intestinal symptoms.
Herbal enemas for ulcerative colitis must be carried out in medical or hospital environments. Before the procedure is undertaken, the lower bowel must be cleaned properly; drip a warm herbal preparation slowly into the colon; let the liquid be retained for at least 4 hours so as to obtain the full herbal effects. Do once a day for ten days, and then rest for 4 days before repeating the treatment. Patients usually feel an improvement after 3 courses. Selection of herbs is based on individual cases, below are some suggested ingredients:
 |
Clearing damp-heat accumulation |
bai tou weng |
Chinese pulsatilla root |
Radix Pulsatillae |
ye ju hua |
wild chrysanthemum |
Flos Chrysanthemi Indici |
pu gong ying |
dandelion |
Herba Taraxaci |
huang lian |
golden thread rhizome |
Rhizoma
Coptidis |
bai jiang cao |
patrinia |
Herbal Patriniae |
 |
Removing blood and qi stagnation |
dan pi |
peony tree root bark |
Crotex Moutan Radicis |
huang qin |
baical skullcap root |
Radix Scutellariae |
huai hua |
pagoda tree flower |
Flos Sophorae |
san chi |
notoginseng |
Radix
Notoginseng |
da huang |
Chinese rhubarb |
Radix et Rhizoma Rhei |
 |
Soothing liver and invigorating spleen |
bai ji |
common bletilla tuber |
Rhizoma
Bletillae |
chai hu |
bupleurum root |
Radix Bupleuri |
bai shao |
white peony root |
Radix Paeoniae Alba |
yu jin |
turmeric root tuber |
Radix Curcumae |
wu yao |
lindera root |
Radix Linderae |
 |
Tonifying spleen and stomach |
huang qi |
astragalus |
Radix Astragali |
dang shen |
pilose asiabell root |
Radix Codonopsis Pilosulae |
bai shu |
largehead atractylodes root |
Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae |
chen pi |
dried tangerine peel |
Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae |
dang gui |
angelica root |
Radix Angelicae Sinensis |
 |
| Pilose asiabell root |
Stimulation of acupoints not only enhances the immune modulation effect, but also mobilizes the innate healing power inside the body. For the localized problems like inflammation, ulcers, muscular spasms and sluggish flow, acupuncture and moxibustion are particular effective and thus facilitate structural recovery.
Suggested acupuncture methods:
Major points: navel's four-point (one-thumb-width apart from the navel, located in three, six, nine & twelve o'clock), tian-shu, guan-yuan & qi-hai;
Assist points: da-chang-shu, zhang-qiang, pi-shu, wei-shu, zu-san-li & san-yin-jiao.
When applying, first punch the four-point needle in 0.3-0.5 cm deep and rotate for about 30 seconds, stimulate the four locations in a clockwise sequence, no needle retention; then select one more major point and 2-3 assist points for stimulation, retain the needles on the locations for 15-20 minutes, moxa cones can be attached for heating during this time. Do this once daily or every two days, ten times is one course.
Moxibustion can also be used to boost the weakened systems, particularly for individuals with chronic symptoms. Below are suggested protocols:
Major points: zhong-wan, tian-shu, guan-yuan & shang-ju-xu;
Assist points: pi-shu, shen-shu, da-chang-shu, zu-san-li, tai-xi, tai-chong, san-yin-jiao & zhong-iv-shu.
Each time, select 1-2 major points and heat for 30-40 minutes; while select 2-3 assist points and heat for 15-20 minutes. Do this once daily or every two days, 15-20 times is one course.
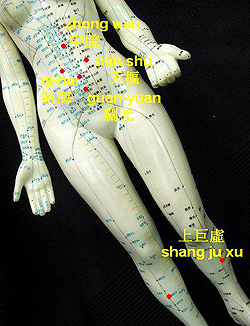 |
| Acupoints for UC |
|