|
An itchy ear is so distressing that you will scratch or probe it without a second thought. However, scratching or probing the ear not only makes the itching worse, it will further irritate the delicate surface of ear canal, increase the risk of infection, and even damage the eardrum. It is a bad habit to scratch or poke your ear with fingers, cotton tips, towels, or other objects. There are many safe ways to manage itchiness inside the ear.
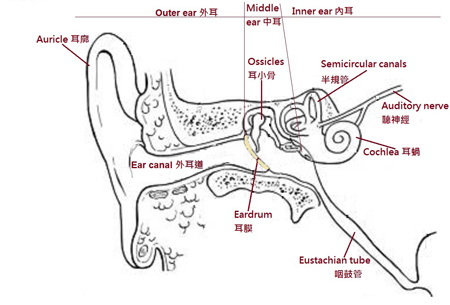
Structures of the ear
|
Causes of itchy ear
When you consult a doctor for constant or intense itchy ear, the diagnosis may be otitis externa, which means an inflammation or infection of the external ear canal, the auricle, or both. The itchy symptom is usually resulted from an irritated skin condition inside the ear. Understanding what caused the irritation can help find an effective way for relief and take preventative actions to keep the ear itch-free in future.
 Earwax: the ear canals are designed to drain wax or debris out itself. It is harmful to clean them by poking with cotton tips or anything else, this will push the earwax deeper rather than remove it. Improper cleaning methods are the most common cause of earwax buildup or blockage. If you have excess earwax production, use a few drops of oil (mineral oil, olive oil or vegetable oil) to clean it. If earwax buildup is still a problem, causing itching and even pain, you should visit a doctor to help remove or for ear drops. The ears need some earwax for lubrication and protection, if they don't produce enough earwax, the ear canals will become dry and itchy too. Earwax: the ear canals are designed to drain wax or debris out itself. It is harmful to clean them by poking with cotton tips or anything else, this will push the earwax deeper rather than remove it. Improper cleaning methods are the most common cause of earwax buildup or blockage. If you have excess earwax production, use a few drops of oil (mineral oil, olive oil or vegetable oil) to clean it. If earwax buildup is still a problem, causing itching and even pain, you should visit a doctor to help remove or for ear drops. The ears need some earwax for lubrication and protection, if they don't produce enough earwax, the ear canals will become dry and itchy too.
 Moisture: it is important to keep the ears free from water. When taking shower or bathing, avoid water running into the ears. If water gets trapped inside the ear, try to drain out by tilting your head to the side, or use a hairdryer to remove the moisture; remember to hold the hairdryer 50cm away and on the lowest setting. Moisture: it is important to keep the ears free from water. When taking shower or bathing, avoid water running into the ears. If water gets trapped inside the ear, try to drain out by tilting your head to the side, or use a hairdryer to remove the moisture; remember to hold the hairdryer 50cm away and on the lowest setting.
 Swimming: swimmers are among the highest risk group to have itchy ear. If you swim regularly, it is advised to wear a swim cap to keep dry, and prevent infections of fungus and bacteria, in particular when the skin of your inner ears is broken or damaged. Swimming: swimmers are among the highest risk group to have itchy ear. If you swim regularly, it is advised to wear a swim cap to keep dry, and prevent infections of fungus and bacteria, in particular when the skin of your inner ears is broken or damaged.
 Chemical irritants: hair and bath products such as hairspray, shampoo, wash gel, bubble bath, or hair dye may get into the ears during a bath or shower, which can cause irritation and itching. Use a cotton ball rolled in Vaseline to cover the entry of the ears if necessary. Chemical irritants: hair and bath products such as hairspray, shampoo, wash gel, bubble bath, or hair dye may get into the ears during a bath or shower, which can cause irritation and itching. Use a cotton ball rolled in Vaseline to cover the entry of the ears if necessary.
 Hearing aids or plugs: don't put on your hearing aids or ear plugs when the ears are wet, because the trapped moisture promotes bacterial or fungal growing. It is not recommended to wear them if you have an infection or other ear skin problems too. Hearing aids or plugs: don't put on your hearing aids or ear plugs when the ears are wet, because the trapped moisture promotes bacterial or fungal growing. It is not recommended to wear them if you have an infection or other ear skin problems too.
 Skin conditions: if you have skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, fungal infection in other areas of the body, they can spread to the ears easily. These conditions may need systemic treatment as well as topical applications. Skin conditions: if you have skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, fungal infection in other areas of the body, they can spread to the ears easily. These conditions may need systemic treatment as well as topical applications.
 Allergens: if you are allergic to certain foods, pollen or dust, then you should consider the itchy ear may be part of the symptoms. Your itchiness may also be due to unfitted jewelries or some cosmetic products. It is better to limit your exposure to the risky allergens, and see a doctor for treatment if necessary. Allergens: if you are allergic to certain foods, pollen or dust, then you should consider the itchy ear may be part of the symptoms. Your itchiness may also be due to unfitted jewelries or some cosmetic products. It is better to limit your exposure to the risky allergens, and see a doctor for treatment if necessary.
In general, the skin inside the ears is very thin, delicate and sensitive, be sure to protect them carefully, unnecessary stimulations are likely to do harm than good. Seek professional advice if you have query about your ear condition.
For occasional itchy ear, you might try this at home: drop a few mild-warm oil into the affected ear canal, let it stay for a few minutes, tilt your head to other side and let the excess oil drain out on a paper towel.
** This method should be used sparingly.
Itchy ear can sometimes be stubborn and persistent. You should go to see an ENT specialist if the itchy ear doesn't improve with time or home care. Chronic ear conditions usually present with following symptoms:
 Constant itchiness in and around the ear Constant itchiness in and around the ear
 Soreness and pain in and around the ear Soreness and pain in and around the ear
 Thickening and flaky skin in the ear canal, even narrowing Thickening and flaky skin in the ear canal, even narrowing
 Discharge from the ear Discharge from the ear
 An affected hearing and also ear ringing An affected hearing and also ear ringing
Chinese herbal prescriptions for itchy ear
Conventional treatment for persistent itchy ear includes a course of specific ear drops and medications. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treats it according to disharmony patterns of individuals
From a TCM holistic view, condition of the ears is associated with internal organs. The ears rely on essence stored in kidney for nourishment, and they are considered as the openings of kidney on the body surface. Lungs support the ears to maintain clean and smooth ear canals. Healthy kidney and lungs ensure the ears to hear accurately. The ears are also important regions for meridians to communicate with each other; all the twelve regular meridians enter or branch out collaterals to the ears. Besides external pathogens, the functional state of body may also take part in forming an itchy ear. TCM physicians will examine the patients and ask them about their overall health condition, medical history, and lifestyles. The remedies for itchy ear are designed to eliminate the localized irritations, and regulate internal organs at the same time.
 |
 |
 |
| Vitex fruit |
Epimedium |
Acorus |
Three common disharmony patterns and the anti-itch remedies for itchy ear are as below.
Pathogens accumulated in ear
Itching or itching and pain in one ear or both ears, and with a strong urge for scratching. There may be a stuffy sensation and whisper ringing in the ear, the ear canal is packed with grey debris that attached with yellow-white mold spots. The ear canal looks red and swelling and may drain out thick discharges after removed the debris. The tongue is red and with greasy coating, and the pulse is taut. TCM remedy should aim to disperse wind, detoxify, clear heat and resolve phlegm.
Sample of prescription: Modified Figwort and Thunberg Fritillary Decoction plus paniculated swallow-wort root, cicada slough and puncturevine caltrop fruit
Blood and qi deficiencies
Intermittent itching inside the ear, the outer ear looks dry and shrunken, and the skin of outer ear and ear canal is rough and flaky. The tongue is pale, and the pulse is taut. TCM remedy should aim to replenish qi and blood, extinguish wind and moist dryness.
Sample of prescription: Modified Rhemannia Rhizome Drink plus cicada slough, belvedere fruit, sopora root
Liver and kidney deficiencies along with pathogen attacking
Severe itching inside the ear, accompanying with stuffy sensation and whisper ringing in the ear. Individuals usually accompany with mental fatigue and lumbar soreness. On examination, the ear canal has grey or yellow color debris, and the skin looks red, flaky and rough after removed the debris. The tongue is pale and the pulse is taut and thready. TCM remedy should aim to invigorate kidney and liver, disperse wind and detoxify.
Sample of prescription: Modified Linking Decoction plus paniculated swallow-wort root, cicada slough and puncturevine caltrop fruit
The above herbal prescriptions are usually provided for oral intake, however they can also be applied as herbal compression. When doing herbal compression, dip a towel in the hot solution and cover it on the affected ear, change another towel when it cools down, do this for 30 minutes every day.
Acupuncture therapy for itchy ear
Acupuncture therapy activates qi and blood flowing, reduces swelling, and stops itching, which can speed up the healing and improve ear functioning. Physicians usually select major points along the triple burner and gall bladder meridians, including ting hui (Gb 2), er men (Sj 21), yi feng (Sj 17), wai guan (Sj 5), and he gu (Li 4). Apply with even techniques and retain the needles for 10 minutes. Stimulating daily, seven days are as one course of treatment.

Acupuncture points for itchy ear
|
Meanwhile, individuals are advised to stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Pickled vegetables, strong-smell meats, seafood, and spicy and pungent food such as leek, garlic, Chinese chive, hot pepper, pepper, leaf mustard, ginger and curry should also be limited.
|