Gout : Definition
Western Medicine
Gout is a metabolic disorder which results in an excess of uric acid in the bloodstream and the deposit of its salts (urates) in the joints, soft tissues and urinary tract. These produce acutely painful attacks of arthritis and soft-tissue inflammation. If untreated, long-term destruction of the joints, formation of tophi in the skin and cartilage, and kidney disease follow. The disorder is more common in men than women and rarely occurs in boys before puberty or women before the menopause.
Uric acid crystals deposited in the joints cause inflammation
Uric acid levels in serum (the clear fluid that separates from blood on clotting) are invariably raised (hyperuremia), although not all those who are hyperuremic will experience attacks of gout. Serum uric acid concentrations are influenced by a number of factors of which age, sex, body-weight and genetic constitution are the most important. Higher levels are found in urban rather than rural communities and are associated with social class, obesity, alcohol consumption and a high protein diet.
Chinese Medicine
Gout is a metabolic disorder which results in raised blood levels of uric acid and the formation of crystals of uric acid salts in the joints. Uric acid is a natural element which results from the normal break down of food and the building up of body tissues. The clinical presentation of gout includes frequent attacks of arthritis, joint deformities, kidney damage and urinary stones.
From a TCM viewpoint, the clinical features of gout, such as frequent attacks of swelling, redness, heat and pain in the joints, and improper movement of limbs, place gout in the category of "bi-syndrome." The ancient TCM classic Suwen (The Book of Plain Questions) states that "bi-syndrome is due to a combined attack of wind, cold and dampness evils." Attacks on the meridians in the superficial areas of the body such as the feet and hands by wind, cold and dampness evils lead to stagnation of vital energy (qi) and blood circulation. It is an obstructive disorder.
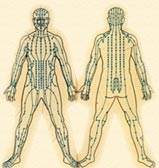
Traditional Chinese medicine holds that there is a distribution network for the fundamental substances like qi, blood and body fluid throughout the body. This network is called the Meridian System. It links organs, limbs, joints, bones, tendons, tissues and skin, and provides communication between the body's interior and exterior.
Meridian system of the body
Gout : Causes
Western Medicine
The raised serum uric acid concentrations seen in gout can result from:
- an increased production of uric acid and/or
- a decrease in uric acid excretion.
Increased production of uric acid occurs in up to one quarter of patients with gout and is common in diseases in which cells are dying and reproducing at a faster rate than normal, such as hemolytic anemia, psoriasis and Paget's disease. Rarely, an enzyme deficiency can cause an increased production of purines. These nitrogen-containing compounds are the metabolic precursors of uric acid.
The reason for decreased uric acid excretion is unknown, but it is thought that obesity, high blood pressure, an abnormally high concentration of fats in the blood, kidney insufficiency, alcohol intake and certain drugs may be involved.
Exercise, starvation, vomiting and toxemia of pregnancy can also be predisposing factors. In more than three-quarters of patients with gout, there is a genetic defect which prevents increased uric acid excretion in response to an increase in purine levels.
Chinese Medicine
Click here to see the causes of gout from a TCM perspective
Gout mainly originates from the invasion and accumulation of pathogens in the meridians. This leads to a disturbance of blood and qi circulation in the limbs. Gout is considered to be caused by both endogenous (originating from inside the body) and exogenous (originating from outside the body) factors.
Exogenous causes
An invasion occurs of external pathogens, such as wind, cold, dampness and heat evils, and these then accumulate in the meridians and joints. TCM practitioners believe that wind, cold or dampness evils invade under the following conditions:
- living or working in cold and damp environments
- getting wet while recreating or being in the rain
- working in water for long periods
- abrupt changes in the weather, and
- exposure to wind while sweating.
Also, when invasive pathogenic evils remain in the body for some time, they develop into internal heat evil. Accumulation of internal heat evil causes a more serious bi-syndrome.
Endogenous causes
Deficiency in vital energy (qi) or stress are considered endogenous causes. Deficiency of vital energy (qi) usually results from an imbalance between work and rest, innate weakness of the body, lack of physical exercise or recent recovery from chronic illness. When the protective qi is under-functioning, the skin and subcutaneous tissues are loosely bonded and exogenous pathogens take advantage of this to invade the body. They accumulate in the meridians and lead to stagnation of blood and qi.
If attacks of bi-syndrome are frequent and lengthy, meridian obstruction and blood stagnation leads to a disturbance in the metabolism of body fluids. Accumulated substances in the fluids are transformed into phlegm and the deeper organs become affected.
Gout : Symptoms
Western Medicine
Gout is characterized by attacks of acute and searing pain in the affected joint, which becomes hot, red and swollen with shiny overlying skin and dilated veins. Gout may be acute or chronic (long term).
Acute gout
In more than 70 per cent of patients, the joint most commonly first affected is that at the base of the large toe. The ankle, knee, the small joints of the feet and hands, the wrist and the elbow are the next most frequently affected, in that order. The main skeleton or large joints such as the hip and shoulder are rarely involved.
The onset of an attack of gout may be slow or extremely sudden. The pain may be sufficient to wake a sufferer from sleep and attacks commonly start at night or in the early hours of the morning. Attacks can sometimes be accompanied by fever and preceded by anorexia, nausea and mood change. If untreated, attacks last a few days or weeks and then subside on their own. Local itching and skin flaking may follow.
Some patients only ever experience a single attack of gout, or have another attack only after an interval of many months or years. However, the tendency is for attacks to recur and to increase in frequency and duration so that they become more or less continuous. Acute attacks may follow dietary excesses, an increase in alcohol consumption, a starvation diet, use of diuretic drugs or by improperly monitored use of drugs used to treat gout. Trauma, excess exercise, surgery or severe illness can also precipitate an attack.
Chronic gout
In patients who experience recurrent attacks of gout, progressive cartilage and bone erosion can take place with deposits of urate crystals occurring in and around the joints and soft tissues. These deposits present as tophi and are often seen on the ears and elbows. If left untreated, a majority of patients with recurrent gout will develop tophi within 10 years and experience subsequent crippling degenerative arthritis.
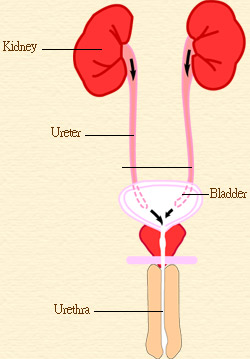
Urate calculi and kidney disease
In a small number of patients, especially in hot climates, urate calculi (stones) develop and can cause renal colic and a decline in kidney function.
Urinary tract
Chinese Medicine
The type or manner of pathogen invasion will result in different presentations of gout bi-syndrome. The main clinical presentation of the predominant invading pathogen is as follows:
- Wind evil causes mobile or unstable joint pain (migratory-bi).
- Cold evil results in localized joint pain (painful-bi).
- Dampness evil produces numbness, heaviness, and swelling of joints and muscles (localized-bi).
- Heat evil generates heat, redness and swelling in the joints and severe tenderness (heat-bi).
TCM practitioners are accustomed to examining the sufferer and categorize symptoms under special syndrome groups known as "disharmony patterns." Certain disharmony patterns present at different stages of gout and are classified as the following types:
Bi-syndrome due to wind, cold and dampness evils
The individual experiences painful joints and limbs, and in some cases severe localized joint pain. Other symptoms include limb heaviness, impaired movement of the affected joints and numbness in muscles. These symptoms will be aggravated during rain or damp weather.
Bi-syndrome due to wind, cold and heat evils
This type of bi-syndrome has an acute onset. The affected joints present with redness, swelling, heat and pain, and also severe tenderness. Relief can be provided with colder temperatures. Other symptoms include thirst, irritability and a fever that is not relieved by sweating.
Bi-syndrome due to phlegm and blood stagnation
This results from repeated attacks of acute bi-syndrome over many years. Individuals present with variable and frequent joint pain, swollen joints, and in severe cases joint deformity. Limbs cannot be flexed or extended and nodules form beneath the skin.
Bi-syndrome with associated liver and kidney damage
Individuals who suffer from long-term bi-syndrome will, without proper treatment, experience migrating bone pain, or soreness and heaviness in the limbs. In severe cases, joint deformity can occur. Symptoms can also include fatigue, pallor, shortness of breath, spontaneous sweating, improper joint movement, limb numbness, and soreness and pain in the loin region.
Gout : Diagnosis
Western Medicine
Although serum urate levels are usually raised in cases of gout, high levels alone are not enough to confirm a diagnosis. Quite commonly, individuals with high serum urate levels never suffer with gout. To make a clinical diagnosis, it is necessary to establish the presence of urate crystals in fluid taken from the affected joint. This is done by examining the fluid under polarized light. Urates show up as needle-shaped crystals.
Sometimes, acute attacks of gout can occur when urate levels are normal. This usually only happens in patients who are receiving treatment for gout or are taking drugs that increase uric acid excretion.
X-ray examination of joints is of little use in diagnosing gout. In chronic cases, characteristic signs of erosion caused by tophi may be seen, but these are often indistinguishable from erosions evident in other forms of arthitis.
Chinese Medicine
Diagnosis in TCM places importance on determining the circumstances and manifestations of a disease through inquiry and symptom observation. Diagnosis is based on the traditional four examination techniques:
- Questioning The TCM practitioner will establish the medical history of both the patient and his family.
- Observation Examination of the physical features of the body, such as the face, tongue, hair, nails, sputum (mucus that is coughed up), and location of pain, all offer clues to the problem. The tongue is a particularly useful indicator of the functioning of the internal organs.
- Listening and smelling The smelling of sputum and breath and listening to the sounds produced by the chest offer additional clues to the patient's health.
- Touching Feeling the pulse is a cornerstone of TCM diagnosis and gives the practitioner much information about any bodily imbalance.
In gout, the procedures used in TCM to differentiate between disharmony patterns can be explained as follows:
Bi-syndrome due to wind, cold and dampness evils
From a TCM viewpoint, when the body's protective qi is weak, climatic and environmental factors (the exogenous evils such as wind, cold and dampness) can readily invade. They attack the superficial meridians and lead to stagnation of vital energy (qi) and blood. Although these three evils may make a combined attack on the body, one is usually dominant and different symptoms result:
Wind evil causes migrating pain involving most limbs and joints.
Cold evil results in localized and severe pain of the limbs and joints (which is relieved by heat and aggravated by cold) and impaired movement of the limbs.
Dampness evil produces heaviness and numbness of the limbs, impaired movement of limbs, joint swelling (but without heat and redness) and localized pain.
On examination, the tongue is coated in a white thin fur. The pulse is tense and wiry, or taut and moderate.
Bi-syndrome due to wind, cold and heat evils
In the conflict between the exogenous evils and vital energy (qi), much heat is produced and the exogenous evils of wind and cold may be transformed into heat evil. Individuals not only suffer from joint and limb discomfort, but also present with general heat symptoms, such as hot and red joints, fever, thirst and sweating. On examination, the tongue is red and covered with yellow fur. The pulse is slippery and rapid.
Bi-syndrome due to phlegm and blood stagnation
In recurrent bi-syndrome, internal damage leads to the formation of phlegm and blood stasis, and symptoms become more serious. Joint pain can worsen and joints become deformed or swollen and movement is impaired. There is severe pain and numbness in the limbs and nodules form beneath the skin. On examination, the tongue is bulky and pink, with bruising, and covered with white and greasy fur. The pulse is thready and uneven.
Bi-syndrome with associated liver and kidney damage
When the circulation of blood and qi is affected over a long period, vital energy (qi) becomes exhausted. The accumulated evils then commonly damage organs such as the liver and kidneys. Individuals usually present with internal damage: fatigue, pallor, shortness of breath, spontaneous sweating, improper joint movement, and soreness and pain in the loin region. On examination, the tongue is pink in color. The pulse is fine or fine and weak.
Gout : Treatment
Western Medicine
Management of gout is accomplished by:
treatment of acute attacks
prevention of future attacks
lowering serum urate levels
Very occasionally surgery is employed to remove large or ulcerating z
Treatment of acute attacks of gout is aimed at providing relief of pain. Three groups of drugs are commonly employed: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine and corticosteroids. Treatment should be started as early as possible and aspirin and diuretics should be avoided. The choice of drug for a particular patient will depend on factors such as timing of attacks, other medication being taken and potential risk of side-effects.
NSAIDs
NSAIDs are the drugs most commonly used in patients who present with gout. Their mechanism of action is complex, but they are very effective. Examples of NSAIDs include indomethacin, diclofenac, ketoprofen and naproxen. Pain relief is usually achieved within two to four hours and treatment is continued for seven to 10 days until symptoms subside. NSAIDs can cause gastric side-effects (stomach-pain, bloating and bleeding) which limit their usefulness, especially in the elderly or those with a history of peptic ulcer disease.
Colchicine
Derived from the meadow saffron, colchicine produces a dramatic response in the treatment of gout, but it has a slow onset of action and causes vomiting and diarrhea in many patients. Colchicine is not an analgesic and has no effect on serum concentrations of uric acid or on its excretion. It is thought to work by reducing the body's inflammatory response to urate crystals. Colchicine is of little use in chronic gout or if many joints are involved. The optimal dose is close to that which causes side-effects and it should be used with great care in the elderly and the debilitated. Colchicine has a role in treating patients for whom NSAIDs are contra-indicated.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids (eg, hydrocortisone) given by injection into the joint can be a useful form of treatment for gout if only one or a few joints are involved. They work by relieving inflammation in the joints. Corticosteroids are not normally given by mouth in gout as they produce inconsistent results, but in certain circumstances (eg, in severe attacks affecting several joints, in kidney disease or heart failure, precluding the use of NSAIDs and colchicine) they may be useful.
Chinese Medicine
Treatment of bi-syndrome in TCM can involve the use of a combination of therapies, such as herbal remedies, acupuncture and qi-gong.
| Herbal therapy |
Bi-syndrome due to wind, cold and dampness evils
Therapeutic aim:To dispel wind, cold and dampness evils, and remove obstructions in the meridians.
Prescription: Modified Yiyiren decoction.
| qiang huo | incised notopterygium rhizome |
| du huo | double-teeth pubescent angelica root |
| fang feng | divaricate saposhnikovia root |
| chuan wu | common monkshood mother root |
| ma huang | ephedra |
| gui zhi | cassia twig |
| yi yi ren | coix seed |
| cang zhu | atractylodes root |
| dang gui | Chinese angelica |
| chuan xiong | Szechwan lovage root |
| sheng jiang | fresh ginger |
| gan cao | liquorice root |
In this prescription, qiang huo, du huo and fang feng help to eliminate wind and dampness evils; chuan wu, ma huang and gui zhi clear cold evil and warm the meridians; yi yi ren and cang zhu tonify the spleen and eliminate dampness evil; dang gui and chuan xiong improve blood production and activate blood circulation; and sheng jiang and gan cao tonify the spleen and middle burner.
Bi-syndrome due to wind, cold and heat evils
Therapeutic aim: To eliminate heat, wind and dampness evils, and remove obstructions in the meridians.
Prescription: Modified Baihu Guizhi decoction
| sheng shi gao | unprocessed gypsum |
| zhi mu | common anemarrhena root |
| gan cao | liquorice root |
| jing mi | polished round-grained rice |
| gui zhi | cassia twig |
In this prescription, sheng shi gao, zhi mu, gan cao and jing mi clear the heat evil and help soothe its symptoms; and gui zhi eliminates the wind evil in the meridians.
Bi-syndrome due to phlegm and blood stagnation
Therapeutic aim: To expel wind evil, remove phlegm, blood stasis and obstructions in meridians.
Prescription: Modified Taohong drink
| tao ren | peach seed |
| hong hua | safflower |
| dang gui wei | Chinese angelica |
| chuan xiong | Szechwan lovage root |
| wei ling xian | Chinese clematis |
In this prescription, tao ren and hong hua activate the blood and eliminate stasis; dang gui wei and chuan xiong activate the blood and improve blood production; wei ling xian eliminates the wind and dampness evils, and removes obstructions in the twelve meridians.
Bi-syndrome associated with liver and kidney damage
Therapeutic aim: To benefit the liverand kidneys, and remove the cold, wind and dampness evils.
Prescription: Modified Duhuo Jisheng decoction
| shu di huang | processed rehmannia root |
| du zhong | eucommia |
| niu xi | achyranthes root |
| sang ji sheng | Chinese taxillus herb |
| ren shen | ginseng |
| fu ling | Indian bread |
| gan cao | liquorice root |
| dang gui | Chinese angelica |
| chuan xiong | Szechwan lovage root |
| du huo | double-teeth pubescent angelica root |
| qin jiao | large-leafed gentian |
| xi xin | Manchurian wild ginger |
| gui zhi | cassia twig |
In this prescription, shu di huang, du zhong, niu xi and sang ji sheng benefit the liver and kidneys, and also strengthen the bones and tendons; ren shen, fu ling and gan cao replenish the vital energy (qi) and tonify the spleen; dang gui and chuan xiong nourish the blood and regulate ying-fen ; du huo, qin jiao, xi xin and gui zhi eliminate the wind, cold and dampness evils and help relieve the bi-syndrome.
| Non-herbal therapy |
Acupuncture and moxibustion
This is generally indicated for chronic bi-syndrome that results in deficiency ofvital energy (qi). For bi-syndrome caused by wind, cold and dampness evils, a combination of acupuncture and moxibustion is recommended. For bi-syndrome caused by wind, cold and heat evils, acupuncture alone is better.
The commonly used acupuncture points for pain relief are:
- Shoulder: jian-zhen and localized trigger-points
- Wrist: yang-chi, wai-guan and he-gu
- Elbow: he-gu, shou-san-li and qu-chi
- Knee: yang-ling-quan and xi-yan duo
- Ankle: zhong-feng, kun-lun, jie-xi and qiu-xu.
Qi-gong
Qi-gong assists in regulating the meridians and anyone with bi-syndrome can benefit from it. It activates the blood circulation and helps restore the balance of yin and yang in the body. Performing qi-gong can increase muscle strength and relieve pain. It also helps rehabilitate damaged joints. Suggested types of qi-qong are fang-song gong and nei-yang gong.
Qi-gong is a breathing exercise that uses mental and physical training techniques for health maintenance and the prevention and treatment of disease. It uses the mind to control the breathing and spirit of the individual.
Gout : Prevention
Western Medicine
Once the symptoms of an acute attack of gout have subsided (spontaneously or with drug use), treatment aimed at the prevention of further attacks should be started. Factors that predispose to high serum urate concentrations and gout include:
- family history
- obesity
- kidney failure
- high blood pressure
- diet high in purines
- alcohol
- diuretic drugs, aspirin
- diseases causing cell breakdown
- lead poisoning.
Although none of these factors on its own may be the cause of high serum-urate levels, modification to lifestyle may help to reduce gouty attacks. For many patients, however, it will be necessary to control urate levels by long-term medication. As this may need to be lifelong, some patients may simply prefer to treat the attacks when they occur.
Medication
- Medication is usually recommended in patients with:
- recurrent attacks of gout
- tophi formation
- kidney complications
- a family history of gout, especially with complications
- an inability to maintain normal urate levels by a change in lifestyle.
If preventive therapy is needed, it can be accomplished in two ways:
- by inhibiting the production of uric acid with allopurinol, or
- by increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid with a uricosuric agent.
Whichever method is used, treatment should not be started until three weeks after the acute attack of gout has subsided.
Allopurinol
Allopurinol is the most commonly used drug for long-term prevention of gout. It is convenient and has few side-effects. It acts by preventing the formation of uric acid from its purine precursors, decreasing levels of urates in the serum and urine, and prevents urate crystals forming in the kidney. It is especially useful for patients who produce too much urate or who have kidney stones or kidney failure.
When therapy is started, acute attacks of gout can occur. The reason for this is not clearly understood, but NSAIDs or colchicine are usually given concurrently for the first few months to avoid such attacks. Allopurinol can occasionally cause a rash, but tolerance usually develops.
Uricosuric agents
Drugs which increase the excretion of uric acid (uricosurics), such as benzbromorone, probencid and sulphinpyrazone, are used if allopurinol cannot be tolerated. Their use is contra-indicated, however, in patients who produce excess uric acid, in kidney failure and in patients with urate stones in the kidney. As with allopurinol, an NSAID or colchicine needs to be given concurrently at first to avoid gouty attacks.
Uricosurics increase the risk of urate crystal formation in the urine (with subsequent formation of kidney stones and loss of kidney function) and should be taken with plenty of water. They can also cause gastro-intestinal upsets and skin rashes. Aspirin must not be taken with uricosuric agents as it interferes with the excretion mechanisms.
Dietary Control
Diet is undoubtedly a contributory factor to high serum-urate levels and modification is important in the prevention of attacks of gout. An attempt to reduce:
- obesity
- excess alcohol intake (especially of beer, port and some wines)
- foods high in purines
should be undertaken by all gout sufferers.
|
||||||||||||
Unless contra-indicated, plenty of water should be taken to flush uric acid through the kidneys. If lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient to ward off attacks, compliance with long-term therapy offers the best chance of avoiding gouty arthritis and the potential damage caused by tophi.
Chinese Medicine
There is no cure for gout. The therapeutic aim is to focus on symptom relief and to control the progress of the disorder. The following measures help to prevent attacks of gout:
Dietary control: eat a balance diet and avoid eating animal organs, bean products and fermented food such as preserved salty fish.
Certain foods should be avoided
Abstain from drinking alcohol.
Abstain from alcohol
Maintain moderate body weight.
Maintain health with exercise
Try to avoid the risk factors of gout, such as stress, over-tiredness, low body temperature and accidents that may damage joints.
Drink plenty of water to encourage the excretion of toxins.
Drink eight glasses of water per day
Western medicine taken for the condition should be on advice of a doctor. Both TCM and Western doctors should be informed of all the therapies being used to relieve gout symptoms.
Individuals with a family history of gout should undergo regular check-ups as they may be predisposed to the disorder.
Regular checkup
Dietary measures
From the TCM viewpoint, both food and drugs come from the same source and food can vary in character. This means that food can promote health or have an adverse effect on it. In TCM, dietetic restraint is urged, meaning that some foods should be avoided in certain disorders or while certain medicines are being taken. For example, intake of salty food should be limited in edematous patients and a greasy diet avoided in cases of diarrhea. In gout, it is bean products, red meat, offal and fermented and salty foods that should be avoided.